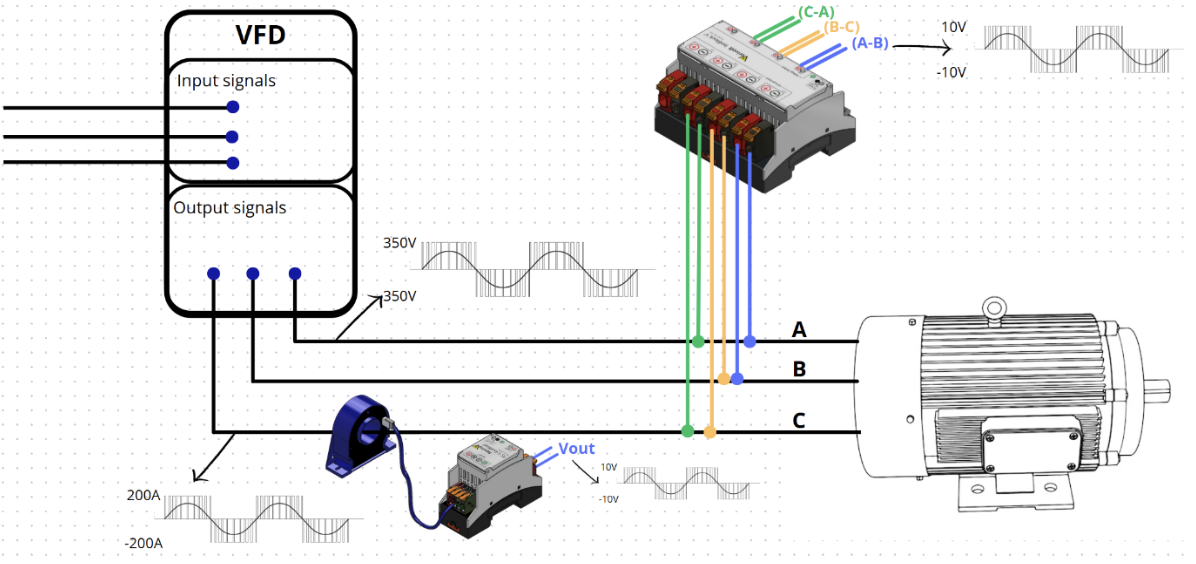
VFD Monitoring
Summary
Verivolt provides reliable sensing solutions for Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) monitoring and testing by offering high-bandwidth, low-noise, and fully isolated voltage and current sensors. Our sensors are engineered to meet the demanding requirements of VFD applications, ensuring accurate, safe, and stable performance in high-frequency and high-voltage environments.
Product in Use
The Challenge: Voltage and Current Monitoring in VFD Systems
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are widely used across various industries to optimize motor performance, enhance energy efficiency, and improve process control. VFDs are commonly found in manufacturing, HVAC systems, water and wastewater treatment, oil and gas, among many others. These applications often involve demanding electrical and environmental conditions, including high currents and voltages required to power motors. Additionally, such environments may expose equipment to high ambient temperatures, electrical noise from switching elements, and mechanical vibrations. Monitoring voltage and current in VFD applications is critical for performance verification, troubleshooting, and preventive maintenance.
Most modern VFDs have embedded sensors that measure current and voltage internally. These internal measurements are primarily used for control logic, protection mechanisms, and sometimes diagnostics. However, there are several good reasons to use independent current and voltage sensors to monitor the motor or load, even if the VFD already has built-in sensing, such as:
Accuracy and Signal Quality
VFD sensors are often optimized for control, not high-resolution or high-accuracy monitoring. External sensors can:
- Offer higher accuracy
- Be calibrated independently
- Provide better linearity and frequency response
- Output analog signals suitable for external data acquisition systems (DAQ, SCADA, etc.)
Accurate Power Measurement
To calculate true power (P = V × I × cosφ), you need both current and voltage measurements. Independent sensors allow real-time power and energy monitoring, including active power (Watts), reactive power (VARs), apparent power (VA) and power factor (cosφ) which are essential for
- Energy efficiency audits
- Load profiling
- Cost allocation
- Diagnosing power quality issues
Advanced Analysis & Logging
VFDs may not provide raw waveform access (especially with high sampling rate), long-term logging and custom data formats or protocols for integration. Independent sensors allow for:
- Real-time waveform capture
- FFT-based harmonic analysis
- Custom integration with other automation or monitoring systems
Third-Party Compliance and Certification
Power quality standards or ISO audits may require certified external measurement tools. Independent sensors ensure traceable calibration and compliance with standards like:
- IEC 61000 (power quality)
- IEEE 519 (harmonics)
- ISO 50001 (energy management)
Retrofit and Test Bench Applications
For testing motors with different VFDs or changing loads, independent sensors:
- Avoid dependency on each VFD’s interface
- Enable standardized data acquisition across brands/models
- Provide portable, reusable instrumentation
Using independent sensors enables several test approached targeting objectives such as:
- Validate Motor Load Performance: Monitor both input and output current to confirm proper motor operation. This helps identify mechanical issues—such as coupling failures, belt loss, or stalled loads—by detecting deviations in current draw under varying load conditions.
- Monitor PWM Voltage Signals: High-frequency PWM output signals from VFDs must be monitored accurately to detect voltage overshoots, dropouts, and anomalies, as well as to evaluate drive performance and ensure that motors receive the correct voltage and frequency levels.
- Detect Voltage Unbalance: Voltage unbalance occurs when the magnitudes of the three-phase voltages are not equal or are out of phase, which can lead to uneven torque, motor overheating, increased losses, and premature equipment failure
- Identify Current Unbalance: Identifying current unbalance is essential for maintaining the health and efficiency of electric motors. An unbalanced current means that the three-phase motor is not receiving equal current in all phases, which can lead to excessive heat, vibration, decreased efficiency, and premature motor failure.
How do Verivolt’s Sensors Address These Challenges?
Verivolt sensors used in this application field present the following characteristics.
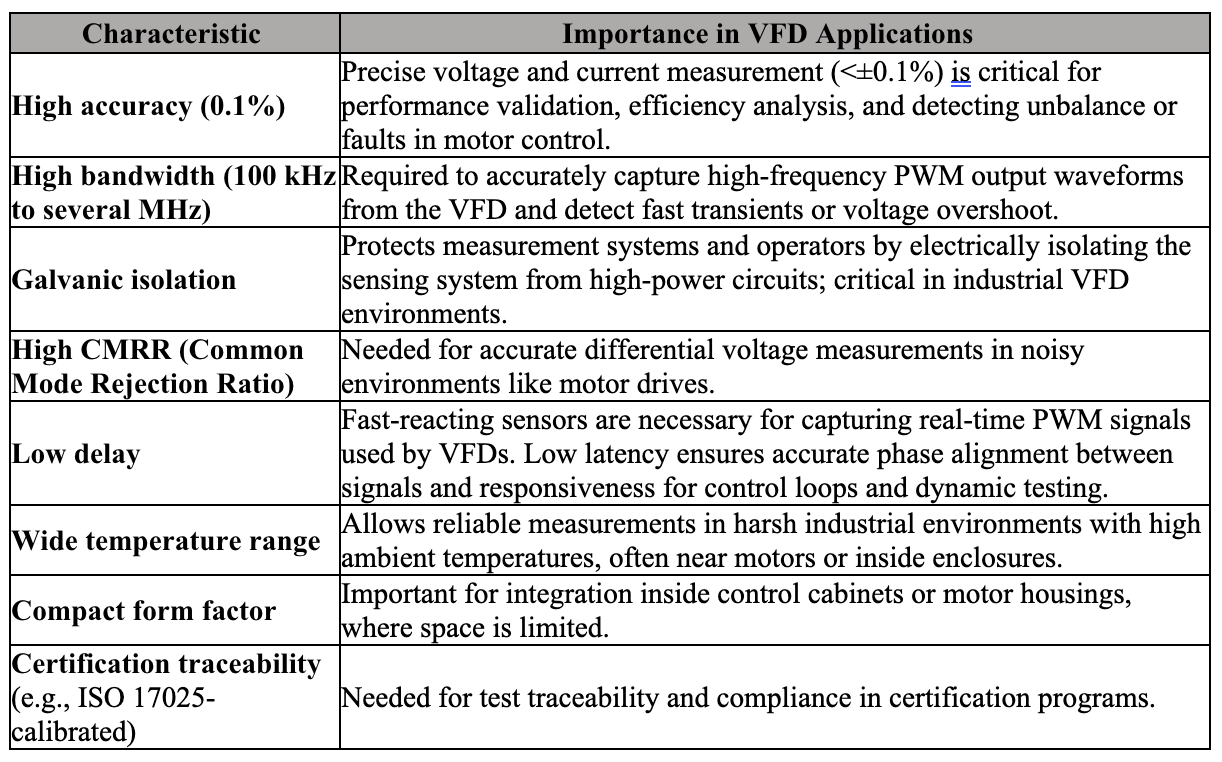
Recommended Verivolt sensors for VFD Applications
Voltage Measurement
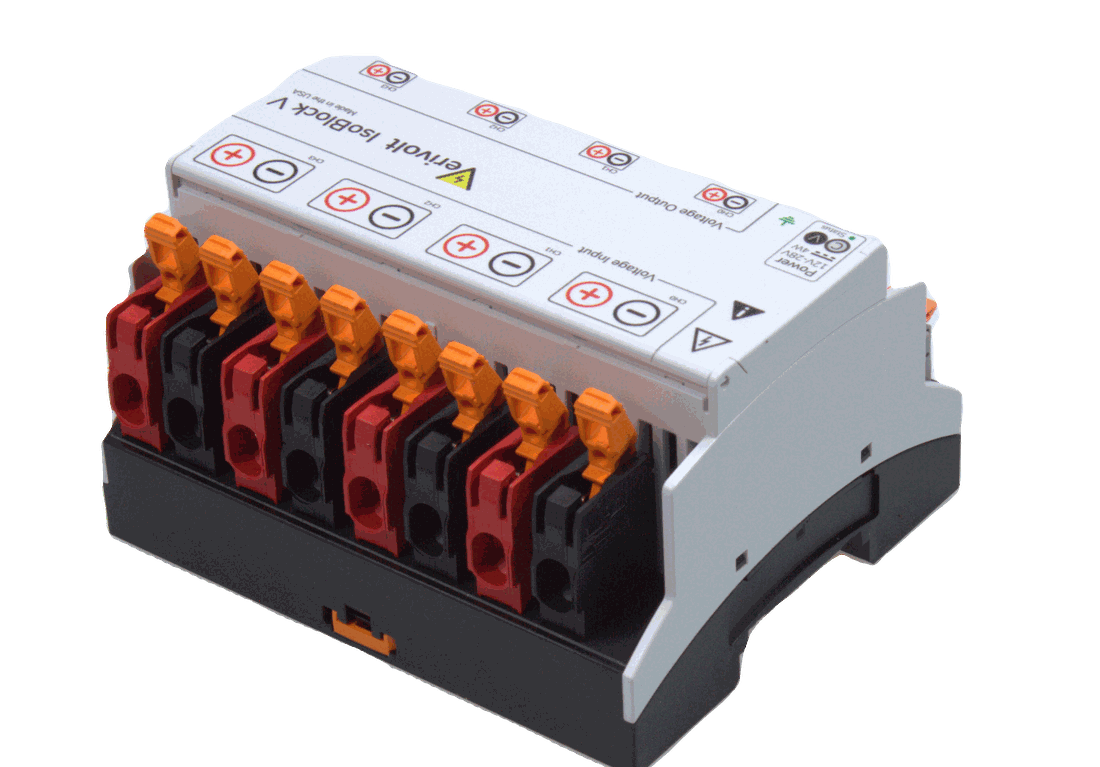
- IsoBlock V-4C (up to 300 KHz – custom): A 4-channel, differential-input, high-bandwidth isolated voltage suitable for capturing line-to-line voltages with ranges from 2V up to 1500V. The IsoBlock V-4C sensor is ideal to monitor the VFD output phases with up to 0.1% accuracy.
- Isoband V (up to 8 MHz): This sensor offers a unique combination of high-isolation, high voltage measurement and high-bandwidth, making it a perfect choice for measuring fast transients, PWM switching and high-frequency signals with 0.2% accuracy.
Your application requires more than 8MHz bandwidth? Try our high-bandwidth, non isolated sensors:
- Entube DE-HB (up to 20 MHz): A high bandwidth differential voltage sensor
- Entube Z (up to 50 MHz): A compact, single ended voltage sensor with the highest bandwidth
Current Measurement
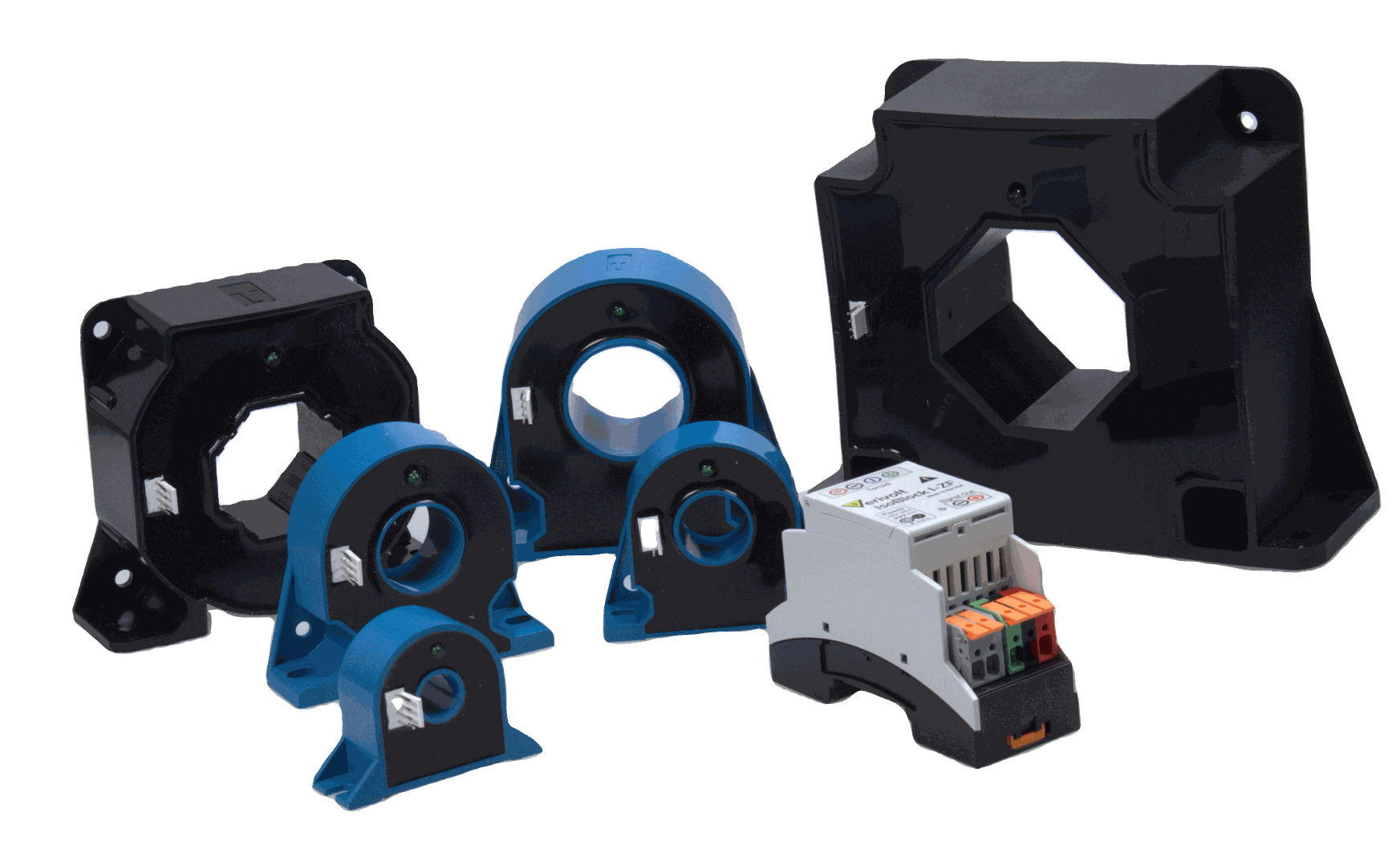
- IsoBlock I-ZF: An isolated, contactless current sensor that uses a zero-flux technique for measurements with up to 0.01% accuracy. Ideal for monitoring both input and output currents and identifying overcurrent or load imbalance. Available from 50A to 2000A ranges.
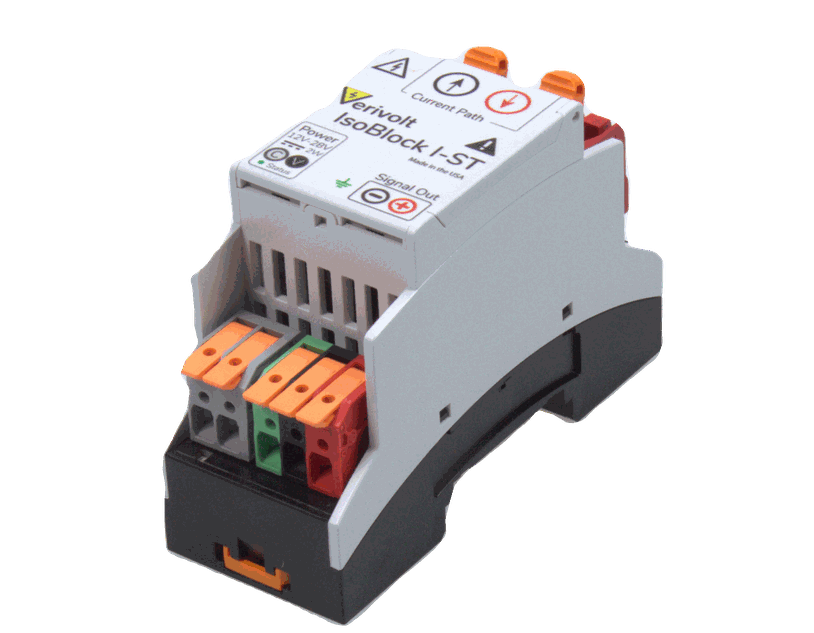
- IsoBlock I-ST: Isolated shunt-based current sensor designed for low to mid range input. Enables simultaneous and isolated monitoring of all three motor phases to detect unbalances. Input ranges available from 100mA to 100A.
Conclusion
Verivolt delivers precision voltage and current sensing solutions tailored for the dynamic requirements of VFD systems. Our sensors provide the performance, accuracy, and isolation needed to ensure optimal motor monitoring. Visit our shop page to explore products designed to meet the evolving challenges of this industry.